What Is DePIN 2025: A Beginner’s Guide to Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks
DePIN – the Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network – is emerging as one of the most prominent trends in the crypto space in 2024–2025. As technology increasingly bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds, the demand for a transparent, flexible, and trustless infrastructure system is growing rapidly. DePIN crypto offers a groundbreaking solution by enabling anyone, anywhere in the world to contribute physical resources such as routers, hard drives, GPUs, or sensors to build decentralized networks. In return, they are rewarded with tokens – creating a fair, transparent, and community-driven operational model.
Unlike traditional infrastructure, which is costly, centralized, and vulnerable to control, DePIN enables cost-sharing, distributes control, and promotes community ownership. From wireless networks, data storage, and digital mapping to high-performance computing – DePIN applications are expanding rapidly and proving their potential to build the next generation of Internet infrastructure.
So, what is DePIN, how does it work, and why is it becoming a key milestone in the decentralized technology revolution? This article will give you a comprehensive answer to all those questions.
What Is DePIN?
DePIN stands for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks—a new class of blockchain projects that bring decentralization to hardware-based services. Unlike traditional blockchain applications that mostly focus on finance, governance, or digital data storage, DePIN projects incentivize users to share physical resources—ranging from network bandwidth and storage space to computing power and mapping data.
In the DePIN ecosystem, the key roles include:
-
Providers:
Individuals or organizations that deploy hardware (e.g., hotspots, servers, sensors). -
Users/Consumers:
Businesses or applications that utilize the infrastructure (e.g., IoT devices, AI workloads, mapping apps). -
Validators/Middleware:
-
Nodes or smart contracts that coordinate resource allocation, verify contributions, and distribute rewards.
These roles interact through blockchain protocols to ensure transparency, fairness, and security. DePIN unlocks massive potential—from community-driven 5G networks to decentralized AI render farms.
How is DePIN different from traditional infrastructure?
To better understand the innovation DePIN brings, let’s compare traditional infrastructure models with decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN) in the table below:
| Criteria |
Traditional Infrastructure |
DePIN (Decentralized) |
| Ownership & Control |
Telecom companies or cloud providers own and control all resources. |
Hardware is community-owned; control is distributed and managed via blockchain. |
| Cost Structure |
Users pay fixed fees for bandwidth and storage, regardless of actual usage. |
Flexible usage-based fees; contributors are rewarded with tokens. |
| Resilience & Redundancy |
Network is vulnerable to outages when a provider fails; limited fault tolerance. |
Distributed network with multiple nodes; if one node fails, others can take over. |
| Scalability & Upgrades |
Requires large capital expenditure (CAPEX) from central entities to expand or upgrade. |
Anyone can scale the network by adding compatible hardware to earn tokens. |
DePIN is not just a technological shift—it’s a revolution in how physical infrastructure is built and operated. By decentralizing ownership and creating fair incentive mechanisms for participants, DePIN paves the way for a new era of community-driven, flexible, and sustainable networks.
Real-world Examples of DePIN:
-
Building decentralized 5G networks:
Individuals can install wireless transmitters at home to help form a mobile or IoT network—without relying on telecom companies. Token rewards are given for providing signal coverage to nearby devices. -
Sharing data storage capacity:
Individuals or organizations can rent out unused storage space to others for storing files, videos, or images—and earn rewards. This provides a decentralized alternative to services like Google Drive or Dropbox. -
Crowdsourced mapping and geodata sharing:
Drivers can mount cameras to capture street-level footage, contributing to an open, decentralized mapping system. Contributors are rewarded as the data is used to update maps. -
Peer-to-peer renewable energy trading:
Households with solar panels can sell excess electricity directly to neighbors through a decentralized energy grid. Transactions are recorded on the blockchain, eliminating the need for utility companies.

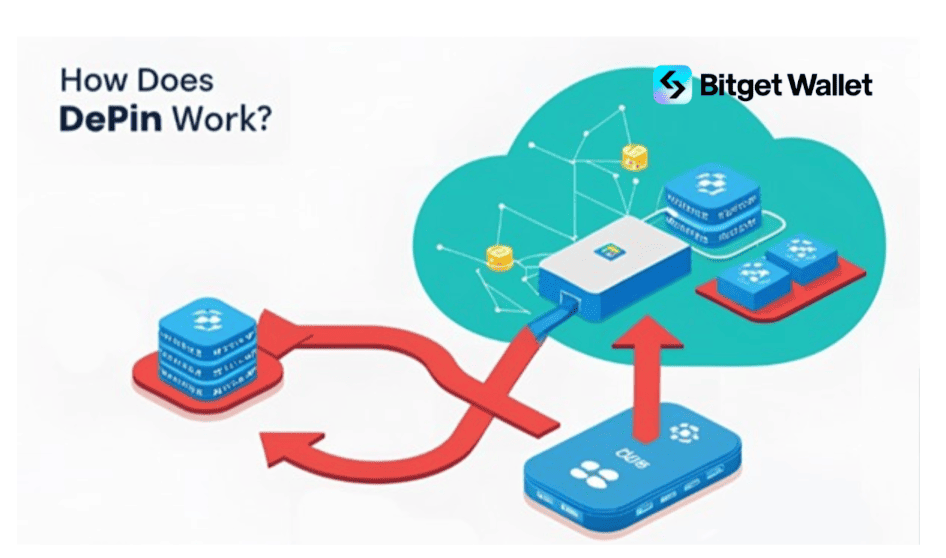
How Does DePIN Work?
DePIN is a model that combines real-world hardware with blockchain technology to build decentralized infrastructure networks. Its architecture consists of three main layers:
1. Hardware Providers
These are individuals or organizations that own and deploy physical devices such as routers, hard drives, GPUs, sensors, or other IoT equipment. They register or lock their devices on the blockchain, linking physical assets to on-chain identities. This enables them to participate in the network and receive rewards based on their contributions.
2. Middleware & Coordination Layer
This layer includes smart contracts or off-chain services responsible for verifying device contributions, measuring performance (e.g., uptime, throughput), and handling disputes. Proof mechanisms such as Helium’s Proof-of-Coverage (PoC) or Filecoin’s Proof-of-Replication (PoRep) ensure data integrity and system reliability.
3. Blockchain Layer
This layer manages token issuance, token transfers, and governance proposals. The blockchain implements incentive mechanisms where contributors receive tokens based on service quality and real-world demand. It also ensures transparency and immutability of transactions and data within the network.
Core DePIN Mechanisms
-
Token Incentives:
Contributors receive network tokens (e.g., $HNT, $FIL) when they provide resources. The tokenomics model is designed to balance supply and demand, maintain network health, and encourage long-term participation. -
Decentralized Governance:
Token holders have voting rights on protocol upgrades, fee structures, and community funds. This ensures the network evolves in line with stakeholder interests and maintains democratic management. -
Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts automatically distribute rewards, enforce service level agreements (SLAs), and process real-time payments. They guarantee that terms and conditions are executed transparently without third-party intervention.
Types of DePIN Projects
DePIN is rapidly expanding with many real-world applications. Below are four representative DePIN projects, each corresponding to a specific use case and utilizing a unique token:
1. Wireless Networks: Helium
-
Overview: Helium is a decentralized wireless network where users deploy Hotspot devices to provide coverage for IoT devices and 5G connectivity. Hotspot operators are rewarded with either HNT or MOBILE tokens depending on the type of service provided.
2. Storage Networks: Filecoin
-
Token: $FIL
-
Overview: Filecoin is a decentralized data storage network where users can rent or offer storage space. Storage providers earn FIL tokens as rewards for delivering reliable storage services.
3. Mapping Networks: Hivemapper
-
Token: $HONEY
-
Overview: Hivemapper is a decentralized mapping network in which users use dashcams to collect street-level imagery. Contributors are rewarded with HONEY tokens for providing high-quality map data.
4. Compute Networks: Render Network
-
Token: $RNDR
-
Overview: Render Network is a decentralized compute platform where creators can rent GPU power for tasks like graphic rendering or AI workloads. GPU owners contribute their computing resources and receive RNDR tokens as rewards.
These DePIN projects highlight the tremendous potential of decentralized technology applied to physical infrastructure, unlocking new opportunities for sustainable and equitable growth in the future.
Benefits of DePIN
The Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) is rapidly emerging as a superior alternative to traditional centralized infrastructure models. By leveraging communities, blockchain technology, and idle hardware, DePIN is not only transforming the way infrastructure is built, but also bringing tangible benefits:
1. True Decentralization
No longer reliant on tech giants or monopolistic providers, DePIN is powered by thousands of individuals and independent organizations around the world. This decentralized network design eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of censorship or service disruption. Power and data are no longer concentrated in the hands of a few, but fairly distributed across the community.
2. Community Ownership
DePIN introduces a token-based incentive model where participants are not just users but also infrastructure owners. They contribute devices and resources and directly benefit from the growth of the network. Every time the network expands or services are used, it's the community—not corporate shareholders—who share in the rewards.
3. Significant Cost Reduction
Instead of spending millions on data centers or transmission towers, DePIN utilizes existing hardware within the community—such as Wi-Fi routers, hard drives, GPUs, and cameras. This dramatically lowers operational costs and promotes healthy competition between providers, leading to fairer service pricing for end users.
4. Balanced Incentive Model
In a DePIN ecosystem, consumers and resource providers connect directly through the blockchain. Token payments are automated and based on service quality and usage volume. High-quality providers are rewarded more, while underperformers earn less—creating a fair, transparent, and performance-driven decentralized network.
5. High Flexibility and Innovation
DePIN is often built on open-source protocols, allowing developers and startups to flexibly integrate new services. Network upgrades are community-driven via voting, rather than dictated by a centralized boardroom—enabling faster, real-world-aligned improvements.
Thanks to these qualities, DePIN is redefining what "infrastructure" means in the digital age—from a centralized, capital-intensive asset into an open, sustainable, and community-owned decentralized network.
Challenges & Risks of DePIN
Although DePIN is opening up a new development direction for decentralized infrastructure, this model still faces numerous technical, social, and legal challenges during the scaling process. Building a decentralized physical network on a global scale is no simple task:
1. Adoption Hurdles
-
Limited hardware deployment:
To ensure effective operation of the DePIN network, a large number of participants are required to provide hardware such as hotspot devices, hard drives, or GPUs. However, convincing the community to install and operate these devices remains a major challenge. -
Complex user experience:
Setting up these devices often requires a certain level of technical knowledge, which poses difficulties for average users. This complexity slows down the widespread adoption and expansion of DePIN networks.
2. Scalability Issues
-
Large-scale physical contribution verification:
DePIN relies on reliable verification mechanisms like Proof-of-Coverage (Helium) or Proof-of-Replication (Filecoin) to ensure contributions are valid. As the network scales, processing massive amounts of data demands high-performance oracle systems and validation algorithms. -
Latency and throughput limitations:
In real-time applications such as decentralized computing or video streaming, latency and throughput become critical factors. DePIN is still working to improve these aspects to meet such demands.
3. Regulatory Risks
-
Compliance with telecom and infrastructure regulations:
Some models like Helium use radio frequencies (e.g., CBRS), which may require specific licenses in many countries. Deploying physical devices on a large scale can also run into infrastructure-related regulatory hurdles. -
Data security and privacy concerns:
In storage or mapping networks like Filecoin and Hivemapper, handling personal data must comply with laws such as GDPR or local security standards, posing significant legal risks for DePIN projects.
Final Thoughts
As we enter 2025, DePIN is solidifying its position as a strategic "intersection" connecting blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and edge computing—a foundation for redefining how humans own, operate, and generate value from physical infrastructure. The core strength of DePIN lies in its ability to democratize essential services such as network connectivity, data storage, digital mapping, and computational power. Instead of relying on tech "giants" or centralized data centers, DePIN empowers communities by transforming everyday devices—from routers and hard drives to GPUs—into profit-generating assets.
DePIN is not merely a fleeting trend—it is the bedrock of a transparent, equitable, and community-centric ecosystem. Whether you are an individual user turning a home Wi-Fi hotspot into a revenue stream, an organization with idle servers, or a developer needing GPUs for AI development—DePIN opens the door to tangible opportunities.
To get started, all you need is a multi-chain wallet like Bitget Wallet—a secure and user-friendly tool for storing and trading top DePIN tokens such as $HNT, $MOBILE, $FIL, $HONEY, and $RNDR. With features like portfolio tracking, hardware staking, and one-tap token swaps, Bitget Wallet is your trusted ally in leveraging the rising wave of decentralized infrastructure.
Let’s build a future together—where every device can become an extension of a decentralized network, owned and governed by you!
FAQs
What is DePIN and why is it important in 2025?
DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network) is a decentralized physical infrastructure model that uses blockchain technology to coordinate resources such as routers, hard drives, GPUs,... provided by the community. In 2025, DePIN becomes important because it brings a transparent, flexible, cost-effective infrastructure solution that does not rely on intermediary organizations.
How does DePIN work?
DePIN operates based on three main layers: The hardware supply layer, where users deploy real devices; The intermediary coordination layer verifies performance and handles rewards; The blockchain layer executes token distribution, data recording, and network governance. All transactions are transparent and automated through smart contracts.
How can I participate in DePIN?
You can participate in DePIN by deploying suitable hardware (for example: 5G hotspot, storage hard drive, computing GPU), registering with the DePIN network, and receiving rewards in tokens. In addition, you need a multi-chain crypto wallet like Bitget Wallet to store and trade DePIN tokens in the most efficient and seamless way.
Risk Disclosure
Please be aware that cryptocurrency trading involves high market risk. Bitget Wallet is not responsible for any trading losses incurred. Always perform your own research and trade responsibly.
- How to Buy LGNS in 2026: A Beginner’s Step-by-Step Guide to Longinus2026-02-04 | 5mins
- How to Buy JYPC in 2026: A Beginner’s Step-by-Step Guide to JPY Coin2026-02-02 | 5mins



















